DVD Ilustrado Multilíngue
The Biology of Prenatal Development
THE BIOLOGY OF PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
English
Baixar Versão em PDF O Que é PDF?
Sumário
- O Período Embrionário (As Primeiras 8 Semanas)
-
- Desenvolvimento Embrionário: As Primeiras 4 Semanas
-
- Capítulo 3 – Fertilização
- Capítulo 4 – DNA, divisão celular e Fator Inicial da Gravidez (EPF)
- Capítulo 5 – Estágios Iniciais (Mórula e Blastocisto) e Células Tronco
- Capítulo 6 – 1 a 1½ Semanas: Implantação e Gonadotrofina Coriônica Humana (hCG)
- Capítulo 7 – A Placenta e o Cordão Umbilical
- Capítulo 8 – Nutrição e Proteção
- Capítulo 9 – 2 a 4 Semanas: Camadas Germinativas e Formação de Órgãos
- Capítulo 10 – 3 a 4 Semanas: O Dobramento do Embrião
- Desenvolvimento Embrionário: 4 a 6 Semanas
-
- Capítulo 11 – 4 Semanas: Líquido Amniótico
- Capítulo 12 – O Coração em Ação
- Capítulo 13 – O Crescimento do Cérebro
- Capítulo 14 – Brotos dos Membros
- Capítulo 15 – 5 Semanas: Hemisférios Cerebrais
- Capítulo 16 – Vias Respiratórias Principais
- Capítulo 17 – Fígado e Rins
- Capítulo 18 – Saco Vitelino e Células Germinativas
- Capítulo 19 – Placas da Mão e Cartilagem
- Desenvolvimento Embrionário: 6 a 8 Semanas
-
- Capítulo 20 – 6 Semanas: Movimento e Sensação
- Capítulo 21 – A Orelha Externa e a Formação de Célula Sanguínea
- Capítulo 22 – O Diafragma e os Intestinos
- Capítulo 23 – Placas da Mão e Ondas Cerebrais
- Capítulo 24 – Formação do Mamilo
- Capítulo 25 – Desenvolvimento dos Membros
- Capítulo 26 – 7 Semanas: Soluços e Resposta a Susto
- Capítulo 27 – O Coração Desenvolvido
- Capítulo 28 – Ovários e Olhos
- Capítulo 29 – Dedos das Mãos e dos Pés
- Um Embrião de 8 Semanas
- O Período Fetal (8 semanas até o Nascimento)
-
- Capítulo 37 – 9 Semanas: Engole, Suspira e se Estica
- Capítulo 38 – 10 Semanas: Revira os olhos e Boceja, Unhas e Impressões Digitais
- Capítulo 39 – 11 Semanas: Absorve Glicose e Água
- Capítulo 40 – 3 a 4 Meses (12 a 16 Semanas): Papilas Gustativas, Movimento de Mandíbula, Reflexo de Sucção, Percepção dos Primeiros Movimentos do Feto
- Capítulo 41 – 4 a 5 Meses (16 a 20 Semanas): Resposta ao Estresse, Verniz Caseoso, Ritmos Circadianos
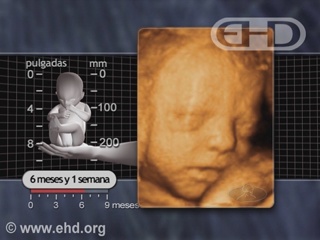
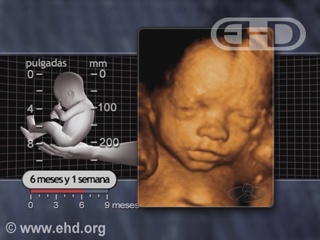
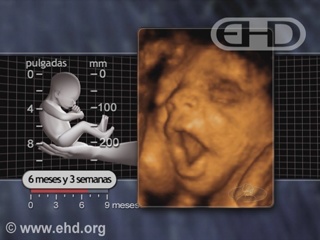
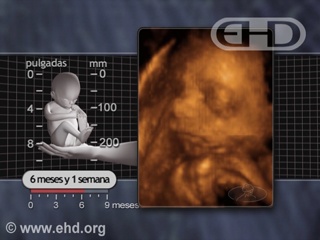
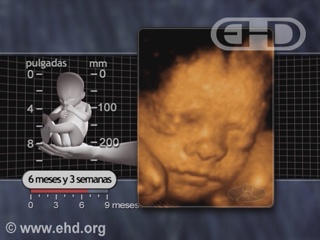
- Capítulo 42 – 5 a 6 Meses (20 a 24 Semanas): Responde ao Som; Cabelo e Pele; Idade de Viabilidade
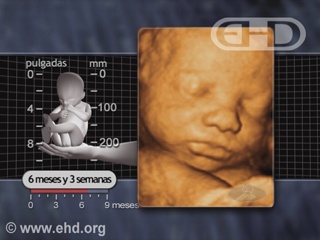
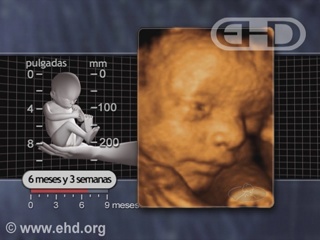
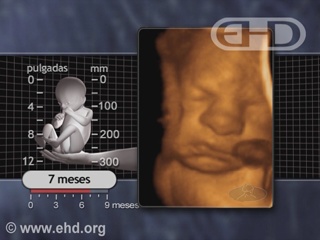
- Capítulo 43 – 6 a 7 Meses (24 a 28 Semanas): Reflexo Cócleo-Palpebral e de Sobressalto; Pupilas Respondem à Luz; Olfato e Paladar
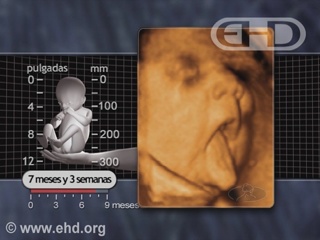
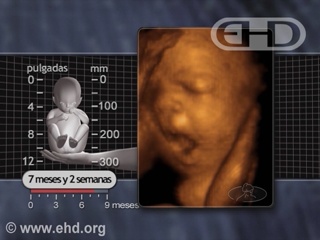
- Capítulo 44 – 7 a 8 Meses (28 a 32 Semanas): Discriminação de Sons, Estados Comportamentais
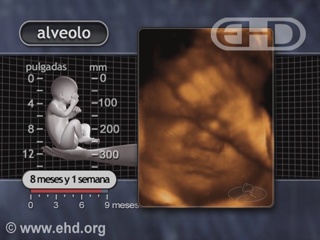
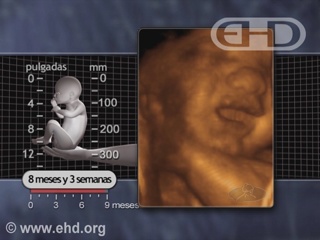
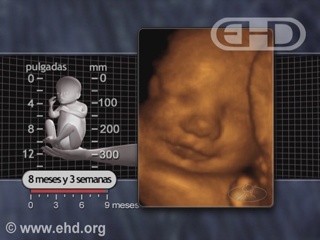
- Capítulo 45 – 8 a 9 Meses (32 a 36 Semanas): Formação dos Alvéolos, Segurar com Força, Preferências de Gosto
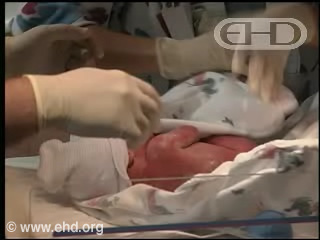
- Capítulo 46 – 9 Meses até o Nascimento (36 Semanas até o Nascimento)